Configuring Database Indexes
In this article we discuss the types of database indexes used by eXist-db and how they are created, configured and maintained. It assumes readers have a basic understanding of XML and XQuery.
Overview
Database indexes are used extensively by eXist-db to facilitate efficient querying of the database. This is accomplished both by system-generated and user-configured database indexes. The current (3.x) version of eXist-db by default includes the following types of indexes:
Properly configured indexes have a huge impact on database performance! Some expressions might run a hundred times faster with an index. This particulary applies to the range index: without a range index, eXist has to do a full scan over the context nodes to look up an element value, which severly limits performance and scalability.
-
Structural Indexes : This index keeps track of the elements, attributes, and the nodal structure of all XML documents in a collection. It is created and maintained automatically. No configuration required.
-
xml:id Index : An index of all
xml:idattribute values is automatically created. These values can be queried byfn:id(). -
New Range Indexes : A (rewritten) range index which provides superior performance on large data sets.
-
Full Text Indexes : This full text indexing module features faster and customizable full text indexing by transparently integrating Lucene into the XQuery engine.
-
NGram Indexes : These map specific text nodes and attributes of the documents in a collection to splitted tokens of n-characters (where n = 3 by default). This is very efficient for exact substring searches and for queries on scripts (mostly non-European ones) which can not be easily split into whitespace separated tokens and are therefore a bad match for the Lucene full text index.
-
Legacy Range Indexes : These map specific text nodes and attributes of documents in a collection to typed values.
-
Spatial Indexes (Experimental): A working proof-of-concept index, which listens for spatial geometries described through the Geography Markup Language (GML). A detailed description of the implementation can be found in the Developer's Guide to Modularized Indexes.
eXist-db features a modularized indexing architecture. Most types of indexes have been moved out of the database core and are maintained as pluggable extensions. The full text, the ngram, the spatial and the new range indexes fall under this category.
Configuring Indexes
eXist-db has no "create index" command. Instead, indexes are configured in
collection-specific configuration files. These files are stored as standard XML
documents in the system collection /db/system/config, which can be
accessed like any other document (e.g. using the Admin interface or Java Client). In addition to defining settings for
indexing collections, the configuration document specifies other collection-specific
settings such as triggers or default permissions.
The contents of the system collection (/db/system/config) should
mirror the hierarchical structure of the main collection. Configurations are shared by
descendants in the hierarchy unless they have their own configuration: the configuration
settings for the child collection override those set for the parent. If no
collection-specific configuration file is created for any document, the global settings
in the main configuration file conf.xml will apply by default. The
conf.xml file should only define the default global index
creation policy.
To configure a given collection, for instance /db/foo, create a
file collection.xconf and store it as
/db/system/config/db/foo/collection.xconf. Note the replication of
the /db/foo hierarchy inside /db/system/config/.
Sub-collections which do not have a collection.xconf file of their
own will be governed by the configuration policy specified for the closest ancestor
collection which does have such a file, so you are not required to specify a
configuration for every collection.
Important:
Configuration settings do not cascade: a sub-collection with
a collection.xconf will not inherit any
settings from any ancestor collection that has a
collection.xconf. If you choose to deploy a
collection.xconf file in a sub-collection, you must specify in
that file all the configuration options you wish to have
applied to that sub-collection (and any sub-collections without
collection.xconf files of their own).
Maintaining Indexes and Re-indexing
The eXist-db index system automatically maintains and updates indexes defined by the user. You do not need to update an index when you update a database document or collection. eXist-db will even update indexes following partial document updates via XUpdate or XQuery Update expressions.
The only exception to eXist-db's automatic update occurs when you add a new index definition to an existing database collection. In this case, the new index settings will only apply to new data added to this collection (or any of its sub-collections) and not to previously existing data. To apply the new settings to the entire collection, you need to trigger a "manual reindex" of the collection being updated.
You can re-index collections using the Java Admin Client. From the Admin menu, select File, Reindex Collection.
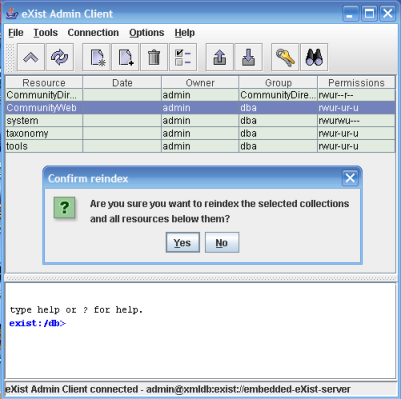
You can also index by passing the following XQuery to eXist-db:
xmldb:reindex('/db/foo')General Configuration Structure and Syntax
Index configuration collection.xconf files are standard XML
documents that have their elements and attributes defined by the eXist-db namespace
http://exist-db.org/collection-config/1.0. The following example shows
a configuration example:
<collection xmlns="http://exist-db.org/collection-config/1.0">
<index>
<!-- Full text index based on Lucene -->
<lucene>
<text qname="SPEECH">
<ignore qname="SPEAKER"/>
</text>
<text qname="TITLE"/>
</lucene>
<!-- Range indexes -->
<range>
<create qname="title" type="xs:string"/>
<create qname="author" type="xs:string"/>
<create qname="year" type="xs:integer"/>
</range>
<!-- N-gram indexes -->
<ngram qname="author"/>
<ngram qname="title"/>
</index>
</collection>All configuration documents have an <index> element directly below the
root element. This encloses the index configuration. Only one
<index> element is permitted in a document. Apart from the index
configuration, the document may also contain settings not related to indexing (e.g.
for triggers). These will not be covered here.
In the <index> element are elements that define the various index types.
Each index type adds its own configuration elements, which are directly forwarded to
the corresponding index implementation. The example above configures three different
types of indexes: full text, range and ngram.
If the document to be indexed uses namespaces, you should add a
xmlns declaration for each of the required namespaces:
<collection xmlns="http://exist-db.org/collection-config/1.0">
<index xmlns:atom="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom">
<lucene>
<text qname="atom:title"/>
</lucene>
<range>
<create qname="atom:id" type="xs:string"/>
</range>
</index>
</collection>The example configuration above creates two indexes on a collection of atom
documents. The two elements which should be indexed are both in the
atom namespace and we therefore need to declare a mapping for
this namespace. Here, the namespace mapping is placed on the <index>
element, but it can appear anywhere in the configuration document.
Check Index Usage
The quickest way to see if an index was used or not is to go to the
Profiling menu item in the Monex
Monitoring and Profiling application.
-
Click on
Enable Tracingto enable usage statistics. -
Run the query you would like to profile. The profiler will collect statistics about any query running on the database instance, no matter how the query is called.
-
Click
Refreshand switch to theIndex Usagetab.
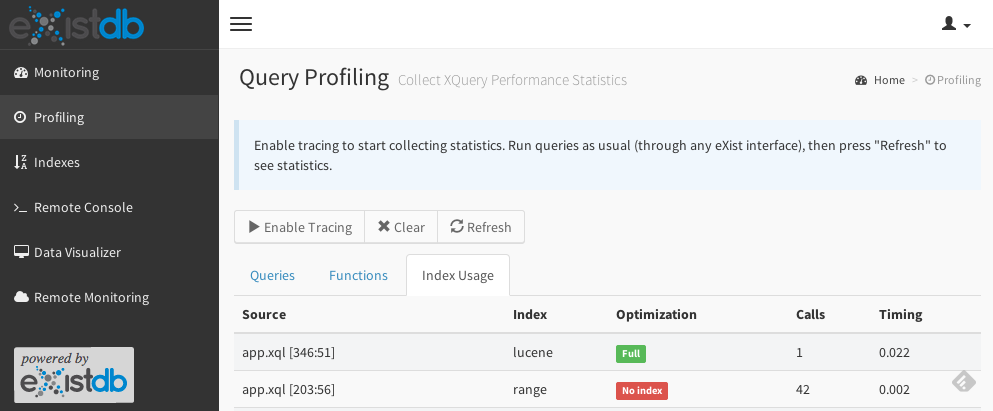
The table provides the following information:
- Source
-
The query containing the expression. The line/column of the expression is given in brackets. For queries stored in the database, the file name will be shown. Dynamically executed queries are displayed with the name "String".
- Index
-
Type of the index used: "range" for the old range index, "new-range" for the new range index, "lucene" for the full text index.
- Optimization
-
- Full
-
The expression was rewritten by the optimizer to make full use of the index. This is the best you can achieve.
- Basic
-
The index was used, but the expression was not rewritten by the optimizer. This is better than "No index" but still several times slower than "Full". Most probably the context of the expression was too complex to rewrite it.
- No index
-
No index defined. Expression is evaluated in "brute force" mode.
- Calls
-
The number of calls to the expression.
- Elapsed time
-
The time elapsed for all calls together. The time is measured for the index lookup only. The absolute numbers are not reliable (due to measurement errors), but they show a tendency: if a lookup takes relatively longer than other expressions, it might be worth to optimize it with an index.
Enabling Index Modules
To activate an index plug-in, it needs to be added to the <modules> section
within the global configuration file conf.xml:
<modules>
<module id="ngram-index" class="org.exist.indexing.ngram.NGramIndex" file="ngram.dbx" n="3"/>
</modules>Every <module> element needs at least an id and
class attribute. The class attribute contains the name of the plug-in
class, which has to be an implementation of
org.exist.indexing.Index.
All other attributes or nested configuration elements below the <module>
element are specific to the implementation and will differ between indexes. They should
be documented by the index implementer.
If an index implementation cannot be loaded from the specified class, the entry will simply be ignored. A warning will be written to the logs.
The Structural index
This index keeps track of the elements (tags), attributes, and nodal structure for all
XML documents in a collection. It is created and maintained automatically in eXist-db,
and can neither be reconfigured nor disabled. The structural index is required for
nearly all XPath and XQuery expressions in eXist-db (with the exception of wildcard-only
expressions such as //*). This index is stored in the database file
structure.dbx.
Technically, the structural index maps every element and attribute
qname (or qualified name) in a document
collection to a list of <documentId, nodeId> pairs. This mapping is used by the
query engine to resolve queries for a given XPath expression.
For example:
//book/section
eXist-db uses two index lookups: the first for the <book> node, and the
second for the <section> node. It then computes the structural
join between these node sets to determine which <section> elements
are in fact children of <book> elements.